Reconciling Account Overview, Process, How It Works
Similarly, if you were expecting an electronic payment in one month, but it didn’t actually clear until a day before or after the end of the month, this could cause a discrepancy. Businesses and individuals may use account reconciliation daily, monthly, quarterly, or annually. Unexplained or mysterious discrepancies may warn of fraud or cooking the books. It provides an opportunity to record their cash position and forecast their cash flow with a higher degree of accuracy. Account reconciliation is a crucial function in business accounting that helps address several fundamental objectives in the accounting process.
Reconciliation ensures that accounting records are accurate, by detecting bookkeeping errors and fraudulent transactions. The differences may sometimes be acceptable due to the timing of payments and deposits, but any unexplained differences may point to potential theft or misuse of funds. For lawyers, reconciliation in accounting is essential what do cash flow statements have to do with liquidity chron com for ensuring that financial records are accurate, consistent, and transparent. While proper reconciliation is the standard for how law firms should handle all financial accounts, it is particularly important—and often required—for the management of trust accounts. And generating financial reports in Clio Accounting is a breeze, making your life, and your accountant’s life that much easier.
Reconciliations are usually performed at the end of an accounting period, such as during the month-end close process, to ensure that all transactions are correctly verified and the closing statements are accurate. Conversely, identify any charges appearing in the bank statement but that have not been captured in the internal cash register. Some of the possible charges include ATM transaction charges, check-printing fees, overdrafts, bank interest, etc. The charges have already been recorded by the bank, but the company does not know about them until the bank statement has been received.
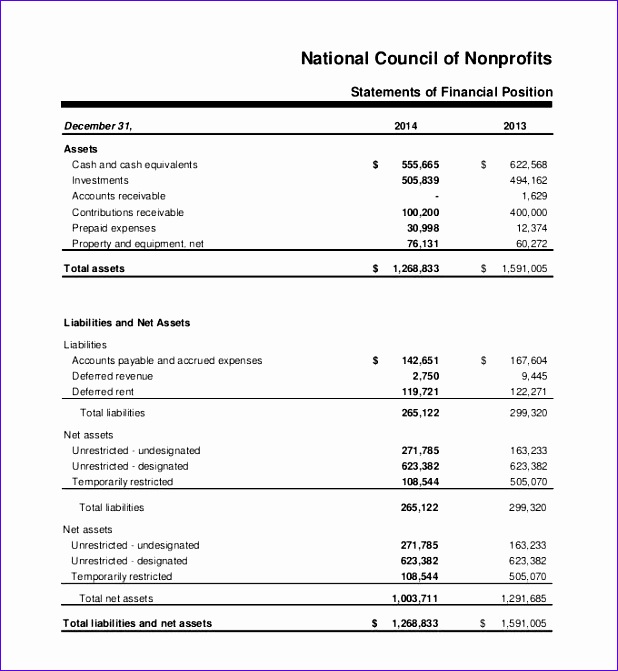
- Once any differences have been identified and rectified, both internal and external records should be equal in order to demonstrate good financial health.
- The account conversion method is where business records such as receipts or canceled checks are simply compared with the entries in the general ledger.
- The document review method involves reviewing existing transactions or documents to make sure that the amount recorded is the amount that was actually spent.
- For example, a company can estimate the amount of expected bad debts in the receivable account to see if it is close to the balance in the allowance for doubtful accounts.
- But there are chances that the check could have bounced due to numerous reasons.
- The more you reconcile any kind of account, the more likely it is that you will pick up discrepancies.
This helps to ensure that the financial records of that unit are accurate and up-to-date. Intercompany reconciliation is a process that occurs between units, divisions, or subsidiaries of the same parent company. This type of reconciliation involves reconciling statements and transactions to ensure that all business units are on the same page financially. The company should ensure that any money coming into the company is recorded in both the cash register and bank statement. If there are receipts recorded in the internal register and missing in the bank statement, add the transactions to the bank statement.
The documentation method determines if the amount captured in the account matches the actual amount spent by the company. Some businesses with a high volume or those that work in industries where the risk of fraud is high may reconcile their bank statements more often (sometimes even daily). In single-entry bookkeeping, every transaction is recorded just once rather than twice, as in double-entry bookkeeping, as either income or an expense. Single-entry bookkeeping is less complicated than double-entry and may be adequate for smaller businesses. Companies with single-entry bookkeeping systems can perform a form of reconciliation by comparing invoices, receipts, and other documentation against the entries in their books. Reconciliation is an accounting procedure that compares two sets of records to check that the figures are correct and in agreement and confirms that accounts in a general ledger are consistent and complete.
What Is Account Reconciliation?
Income tax liabilities are reconciled through a schedule to compare balances with the general ledger. Adjustments are made as necessary to reflect any differences via journal entries. For example, Company XYZ is an investment fund that acquires at least three to five start-up companies each year. For the current year, the company estimates that annual revenue will be $100 million, based on its historical account activity.
Benefits of Account Reconciliation
Account reconciliation is a critical financial process that ensures the accuracy and consistency of an organization’s financial records. By comparing internal financial statements with external sources, such as bank statements, businesses can identify discrepancies, correct errors, and maintain financial integrity. Reconciling your bank statements simply means comparing your internal financial records against the records provided to you by your bank. This process is important because it ensures that you can identify any unusual transactions caused by fraud or accounting errors.
Bank Reconciliation
The account conversion method is where business records such as receipts or canceled checks are simply compared with the entries in the general ledger. The process is important because it ensures that you can weed out any unusual transactions caused by fraud or accounting errors. The process is particularly valuable for companies that offer credit options to their customers.
How Precision Neuroscience streamlined systems and slashed data entry with Ramp
Analytics review uses previous account activity levels or historical activity to estimate the amount that should be recorded in the account. It looks at the cash account or bank statement to identify any irregularity, balance sheet errors, or fraudulent activity. However, generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) require double-entry bookkeeping—where a transaction is entered into the general ledger in two places.